You’ll find that hot water radiators provide steady, quiet heat with better energy efficiency and lower maintenance. They are ideal for modern or humid environments.
Steam radiators offer rapid, high-capacity heat and increased humidity. This makes them suitable for older buildings in cold, dry climates but they require more upkeep and careful installation.
Each system impacts indoor air quality and comfort differently. Installation and design considerations also shape your choice. Exploring these factors will help you determine the best fit for your building and climate.
- Efficient Heating: The 10-piece heater(28.54×3.66×22.36 in ) can produce up to 5,768 BTUs of heat….
- Premium Quality: The wall-mounted heater is constructed from high-quality, scratch free aluminum,…
- Quality Performance: Plumbing system heating operates quietly and with stable efficiency, consuming…
- SIZES: Available in multiple sizes
- INSTALATION: Free- standing,
- EFFICIENCY: Efficient radiator replacement option, Cast iron provides very quiet operation
Key Takeaways
- Steam radiators provide rapid, high-temperature heat with increased humidity, ideal for older buildings in cold, dry climates.
- Hot water radiators deliver steady, even heat with neutral moisture, suited for modern homes and humid or moderate climates.
- Steam systems require complex maintenance and skilled installation, while hot water systems are simpler, quieter, and easier to maintain.
- Steam radiators are larger and vintage-styled, whereas hot water radiators are compact, flexible, and blend with modern interiors.
- Hot water systems operate more energy-efficiently with lower heat loss and precise control compared to steam systems.
Hot Water & Steam Radiator: Side-by-Side Performance Analysis
| Feature | Hot Water Radiators | Steam Radiators |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | 140°F – 180°F | 212°F (boiling point) |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher efficiency – lower operating costs | Moderate efficiency – higher energy use |
| Heat Distribution | Steady, even heat throughout space | Rapid, intense heat with some variation |
| Noise Level | Virtually silent operation | Banging, hammering sounds common |
| Humidity Impact | Neutral – no moisture added | Increases humidity naturally |
| Maintenance Requirements | Lower maintenance – annual checkups | Higher maintenance – frequent inspections |
| Installation Complexity | Simpler installation – flexible layouts | Complex installation – precise slope requirements |
| Best Climate Match | Humid or moderate climates | Cold, dry climates |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront investment | Higher initial costs |
| Building Type | Modern homes and new construction | Historic buildings and older structures |
| Temperature Control | Precise zone control available | Limited control options |
| Safety Considerations | Lower pressure – safer operation | Banging, hammering sounds are common |
How Steam and Hot Water Radiators Operate?

Although both steam and hot water radiators serve the purpose of heating spaces, they operate on fundamentally different principles. Steam radiators rely on pressurized steam generated at 212°F to transfer heat through condensation.
Hot water radiators, on the other hand, circulate water heated between 140°F and 180°F using pumps. These pumps maintain steady flow and gradual heat distribution throughout the system.
In steam systems, steam travels quickly through pipes driven by pressure differentials. It enters radiators and displaces air via vents before condensing and returning as water.
Hot water systems use pumps to push heated water through metal radiators. These radiators transfer heat by conduction and radiation, aided by fins that increase surface area.
Both systems generate natural convection currents. However, steam radiators deliver rapid, high latent heat output, whereas hot water radiators provide consistent sensible heat, ensuring gradual warming.
Energy Efficiency Comparison Between Systems
When comparing energy efficiency between steam and hot water radiator systems, you’ll find that operating temperatures and heat transfer mechanisms play critical roles.
Hot water systems operate below 100°C, reducing energy consumption by requiring less heat input than steam systems, which must boil water at 100°C. However, improper maintenance such as a blocked hose in related heating equipment can impair efficiency over time.
Hot water heating uses lower temperatures than steam, cutting energy use by needing less heat input. Although steam transfers heat rapidly through latent heat during condensation, it incurs greater energy losses during start-up and piping.
Hot water systems maintain steady, even heat via sensible heat transfer with continuous circulation, minimizing heat loss and enabling precise temperature modulation. This results in lower fuel consumption and enhanced boiler efficiency.
While steam systems excel in fast heat distribution for large buildings, their higher operating temperatures and venting losses can increase overall energy costs.
Steam systems also provide built-in humidification benefits, which can be advantageous in dry climates. Therefore, hot water systems generally deliver superior long-term energy efficiency through reduced heat loss and optimized controls.
Maintenance Needs and System Reliability

Since steam radiator systems operate under higher pressures and temperatures than hot water systems, they demand more frequent and detailed maintenance to guarantee safe and efficient operation.
You’ll need to regularly inspect steam traps, air vents, and boiler water levels to prevent water hammer, pressure surges, or explosion risks. Prompt leak repairs are critical to avoid structural damage. Hot water systems require annual checks of circulator pumps, system pressure, and periodic flushing to remove sediment and maintain flow.
Avoid running pumps without sufficient water to prevent pump damage. Although hot water systems have more mechanical parts prone to wear, steam systems, when properly balanced, can operate reliably for decades.
Both systems benefit from professional servicing to optimize longevity and reliability, but steam setups inherently involve higher maintenance complexity and safety vigilance due to their operating conditions. Additionally, seasonal boiler start-up and water level checks are essential maintenance tasks specific to steam systems.
Impact on Indoor Air Quality and Comfort
You’ll notice steam radiators increase indoor humidity, which can enhance comfort but also risk mold if unmanaged. This added moisture is beneficial for respiratory and skin conditions. Hot water radiators maintain more stable, neutral moisture levels.
Noise and pipe vibrations from steam systems may cause minor disruptions, whereas hot water systems operate quietly, preserving a calm environment. Additionally, hot water radiators provide more consistent temperature control, reducing hot spots common in steam heating.
Humidity Levels Effects
Although both steam and hot water radiators serve to heat indoor spaces, their effects on humidity levels—and consequently on indoor air quality and comfort—differ markedly.
Steam radiators can slightly increase indoor humidity during initial heating by releasing moisture through steam condensation and evaporation. This moisture boost benefits dry climates by mitigating dryness-related discomfort but risks promoting mold growth in already humid environments.
Additionally, steam boilers operate at higher pressures, which contributes to their capacity to generate and distribute steam effectively. It is important to regularly inspect the valve to ensure optimal performance and avoid leaks that could affect system efficiency.
Conversely, hot water radiators don’t add moisture, maintaining neutral humidity levels and reducing moisture-related issues in humid areas. Both systems cause relative humidity to drop as warm air holds more moisture, but steam’s higher surface temperature induces more convection, affecting perceived humidity and air movement.
To optimize comfort, you must consider your local climate and possibly supplement humidification when using hot water radiators in dry conditions.
Noise and Disruption
How does the noise generated by steam and hot water radiators affect your indoor environment? Steam radiators produce loud banging, hammering, and popping sounds due to rapid steam condensation, trapped water, and pipe expansion.
These noises disrupt occupant comfort, especially in quiet settings, causing stress and sleep disturbances. The steam heating process, where water heated in a central boiler evaporates into steam, is fundamental to how these radiators function and contribute to noise generation.
Such noise often prompts you to open windows or increase ventilation, potentially altering indoor air quality unnecessarily.
In contrast, hot water radiators operate quietly, with minimal sound from water circulation pumps or valve adjustments. This fosters a calm atmosphere conducive to relaxation and productivity.
Furthermore, steam radiator noise signals mechanical imbalances, requiring maintenance to prevent further disruptions. Hot water systems have fewer mechanical noise issues, reducing interruptions and maintenance needs.
Temperature Consistency
While noise levels influence occupant comfort, the consistency of heat delivery plays an equally important role in maintaining indoor air quality and thermal stability.
Hot water radiators excel here, providing steady, even heat through constant water circulation at regulated temperatures. This minimizes temperature fluctuations and air stratification. The output ratio of hot water radiators, which improves with stable water temperatures, helps ensure efficient and consistent heating performance. This stable circulation also helps prevent airlock issues that can disrupt heating efficiency.
This stability reduces cold drafts and prevents the localized hot and cold spots common with steam systems. Steam systems heat unevenly because steam follows paths of least resistance and cycles between hot and cold phases.
Consequently, hot water systems maintain more uniform humidity levels, reducing respiratory stress risks. In contrast, steam radiators’ rapid heat-up and cyclical heating create temperature gradients that can degrade thermal comfort and air quality.
Additionally, their moisture addition risks mold growth in poorly ventilated areas. Therefore, hot water radiators offer superior temperature control, enhancing overall indoor comfort and air quality.
Installation Challenges and Cost Factors
Because steam radiator systems demand intricate plumbing and precise installation techniques, you’ll face greater complexity and higher labor costs compared to hot water radiator systems.
Steam systems require carefully sloped pipes for condensate return, accurate vent placement, and robust boilers sized for rapid steam generation. You’ll also need skilled labor familiar with steam-specific nuances like air venting and trap installation, which prolong installation time and increase expenses.
Conversely, hot water systems use simpler piping with smaller diameters, flexible layouts, and efficient boilers operating at lower pressures, reducing both material and labor costs.
Additionally, hot water systems avoid condensate pumps and specialized traps, further lowering upfront and maintenance costs.
Installation scheduling favors hot water setups due to straightforward balancing and fewer critical parameters. This enables quicker project completion with less risk of costly errors.
Moreover, understanding the pressure energy accumulation in stages is crucial to optimizing system efficiency and ensuring reliable operation.
Design and Aesthetic Considerations
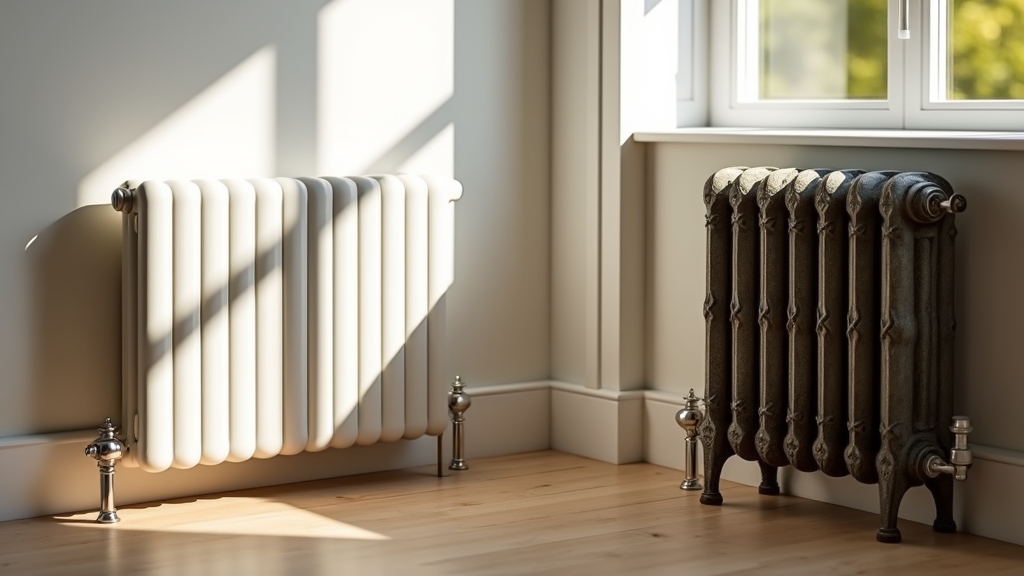

What sets steam and hot water radiators apart in design and aesthetics hinges on their fundamental operational differences.
Steam radiators feature larger, bulkier cast iron sections with nipples only along the bottom, supporting steam’s upward displacement and giving a uniform, vertical profile favored in vintage settings. Proper setup and maintenance of these radiators are essential to prevent banging noises and leaks, ensuring reliable and efficient operation. It is also important to periodically drain the water inside the system to maintain performance and avoid damage.
Hot water radiators, by contrast, have top and bottom nipples enabling continuous water circulation. This allows for more compact, finned designs that can be oriented vertically or horizontally. Such designs enhance heat transfer efficiency and offer diverse modern styles with various materials and finishes.
Steam radiators often dominate room aesthetics due to their size, influencing furniture layout. Their presence is typically more pronounced, making them a focal point in a room.
On the other hand, hot water radiators integrate discreetly in confined spaces. They provide greater spatial flexibility and tend to blend more easily with contemporary interiors.
When to Choose Steam or Hot Water Heating?
You should consider steam heating if your building is older and located in a dry climate where added humidity improves comfort and air quality. Steam systems also provide a higher heat-carrying capacity, enabling efficient heat transfer in large or multi-floor buildings.
Conversely, hot water systems suit newer constructions or humid environments due to their consistent heat and moisture-neutral operation. Evaluating the building’s age and local climate will guide you toward the most efficient and effective system choice.
Additionally, the efficient impeller design in modern pumps can optimize water circulation in heating systems.
Climate and Humidity Needs
When selecting between steam and hot water heating systems, you must consider both climate and indoor humidity needs to guarantee ideal performance and comfort.
Steam heating excels in cold, dry climates by delivering rapid, high-temperature heat and adding moisture, which can alleviate dry indoor air. However, in humid or milder climates, steam risks overheating and excess moisture buildup.
Hot water systems perform best in moderate or humid climates, providing stable, lower-temperature heat without raising indoor humidity, reducing condensation risks.
To choose appropriately, evaluate these factors:
- Steam suits harsh winters needing quick heat and humidity addition.
- Hot water fits regions with moderate temperatures and moisture sensitivity.
- Steam requires precise control to avoid indoor humidity problems.
- Hot water enables zoned heating and consistent moisture levels, making it especially suitable for temperature control.
Building Type and Age
Selecting between steam and hot water heating also depends heavily on the building’s type and age, as these factors influence system compatibility, efficiency, and maintenance requirements.
If you’re working with early 20th-century or older buildings, steam systems often dominate due to existing infrastructure and high thermal mass. However, they require frequent valve maintenance and may have uneven heat distribution.
Mid-century multifamily buildings increasingly favored convertible steam/hot water radiators. Hot water systems offer better zoning and efficiency but necessitate radiator upgrades.
For post-war suburban homes and new constructions, hot water heating is standard. It delivers faster temperature response, easier zoning, and compatibility with modern HVAC and energy sources.
Historic or heritage buildings typically retain steam systems to preserve architectural integrity, despite retrofit challenges. Your choice must reflect these structural and operational nuances for optimal performance.
Additionally, regularly adjusting pressure regulators in hot water systems can prevent common issues and maintain efficient heating performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Steam Radiators Be Used With Renewable Energy Sources?
Yes, you can use steam radiators with renewable energy sources, but you’ll need to upgrade your system. Adding thermostatic radiator valves and improving venting helps reduce steam consumption, making it more efficient.
Retrofitting steam boilers to run on biomass or renewable electricity lowers carbon emissions. However, steam systems require careful pressure control and venting adjustments. While challenging, these modifications enable practical integration of renewables in your existing steam radiator setup.
How Do Steam and Hot Water Systems Affect Home Resale Value?
You’ll find that steam systems can boost resale value in historic neighborhoods by adding charm, but their complex maintenance and higher service costs may deter buyers.
Hot water systems often enhance value due to reliable, efficient heating and easier upkeep, appealing to modern buyers. Installing energy-efficient hydronic systems can increase appeal.
Ultimately, resale impact depends on your market’s preference for historic authenticity versus contemporary comfort and efficiency.
Are There Safety Risks Unique to Steam Radiator Systems?
Yes, steam radiator systems pose unique safety risks you need to manage carefully. Their high-pressure steam can cause burns or pipe bursts if valves or vents fail.
Older systems might contain asbestos insulation or lead-based paint, increasing health hazards. Airlocks and water hammer effects can exacerbate mechanical stress, risking component failure.
You must perform regular inspections, maintain proper clearance, and replace hazardous materials promptly to guarantee safe operation.
What Is the Typical Lifespan of Steam Versus Hot Water Boilers?
You’ll find steam boilers typically last 20 to 30 years with proper care, while hot water boilers tend to last 1 to 5 years longer. You should note cast iron water boilers in hot water systems can exceed 20 years, sometimes reaching 50.
You must maintain both regularly, but be aware high-efficiency models often have shorter lifespans around 15 years due to corrosive internal conditions. Proper sizing, installation, and maintenance directly affect longevity.
Can Hot Water Radiators Be Integrated With Smart Home Systems?
Yes, you can integrate hot water radiators with smart home systems using smart thermostatic valves and compatible controllers. These valves allow you to control temperature remotely via apps, set room-specific schedules, and create multi-zone heating zones.
They support protocols like Z-Wave or Zigbee, enabling seamless communication with home automation hubs and voice assistants. Installation is straightforward, and features like window-open detection and child locks enhance safety and energy efficiency.
Choose the Right Radiator Type for Maximum Comfort
Choosing between hot water and steam radiators isn’t unlike steering between the steady current of a river and the powerful surge of a waterfall. You’ll weigh energy efficiency, maintenance demands, and installation costs with care.
While hot water systems offer precise control and quieter operation, steam radiators deliver robust heat with classic reliability. Ultimately, your decision hinges on your space’s needs and your comfort priorities—select wisely to harness warmth that’s both efficient and enduring.
- Efficient Heating: The 6-piece heater can produce up to 3,461 BTUs of heat. Side air vents are…
- Premium Quality: The wall-mounted heater is constructed from high-quality, scratch free aluminum,…
- Quality Performance: Plumbing system heating operates quietly and with stable efficiency, consuming…
- SIZES: Available in multiple sizes
- INSTALATION: Free- standing,
- EFFICIENCY: Efficient radiator replacement option, Cast iron provides very quiet operation
Last update on 2026-03-02 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API