Last Updated on July 9, 2025
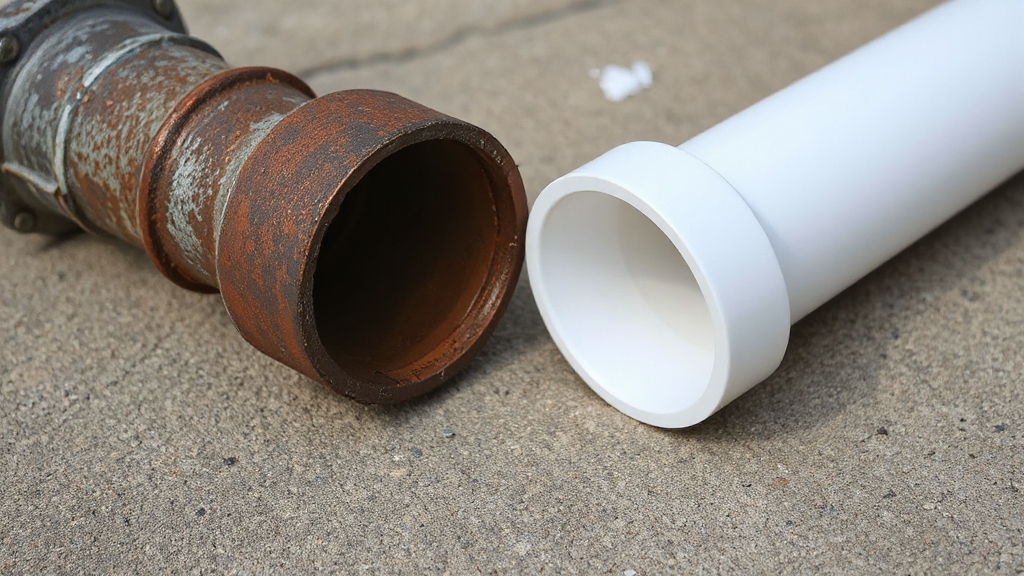
When choosing between cast iron and PVC, you’ll trade off cost, weight, and durability. PVC is lighter, easier to install, and more affordable upfront, with strong corrosion resistance but lower temperature tolerance.
Cast iron handles heat better, offers superior fire resistance, and excels under heavy-duty use, but it’s heavier, pricier, and can corrode over time.
Your decision depends on project conditions, chemical exposure, and budget constraints—understanding these factors will help clarify which material fits your needs best.
- VENTRAL PVC: Pipe and Pressure Fittings are used in irrigation, underground sprinkler systems, swim…
- MADE IN THE USA: For over a century, Ventral has been fabricating pipe and fittings, employing more…
- EASY INSTALLATION: White fittings that are used in potable water applications only; They are…
- 1/2 INCH X 12 INCH BLACK PIPE NIPPLE 6 PACK: Design ambitious projects for your bedroom, bathroom,…
- UNLEASH YOUR CREATIVITY and bring the vintage industrial style into your home, office, garage,…
- HIGH QUALITY, DURABLE INDUSTRIAL PIPE FITTINGS. You will know Pipe Décor parts and accessories when…
Key Takeaways
- PVC pipes are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easier to install, making them more cost-effective for most plumbing projects than heavy, rigid cast iron.
- Cast iron offers superior durability, fire resistance, and noise reduction, lasting 50–100 years but requiring more labor and specialized handling.
- PVC’s flexibility allows it to absorb ground movement and simplifies installation in confined spaces, unlike the rigid, brittle cast iron.
- Cast iron is preferred for high-temperature applications due to its thermal resistance, while PVC deforms above 140°F and emits toxic fumes if burned.
- Environmental impact varies: cast iron has a higher carbon footprint in production, while PVC manufacturing releases toxic chemicals but benefits from lighter transport emissions.
Cast Iron vs PVC Pipe Comparison
| Feature | Cast Iron | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | $12.50-30 per linear foot | $0.60-7.50 per linear foot |
| Installation | Complex – requires skilled labor | Simple – basic tools, easy handling |
| Durability | 50-100 years | 50-100 years |
| Weight | Heavy – needs equipment/multiple workers | Lightweight – manual handling |
| Temperature Limit | Exceeds 212°F | 140°F maximum |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent – fire resistant | Poor – toxic fumes when burned |
| Corrosion | Moderate – prone to rust | Excellent – corrosion resistant |
| Maintenance | High – frequent inspections needed | Low – minimal upkeep required |
| Noise Level | Quieter – 6-10 dB lower | Noisier – requires sound dampening |
Cost Comparison Between Cast Iron and PVC
When comparing costs between cast iron and PVC pipes, it’s clear that PVC offers a considerably lower upfront material price, starting as low as $0.50 per linear foot versus cast iron’s $10 to $20 range before markup.
However, maintenance requirements such as cleaning or replacement should also be considered when evaluating total cost differences, especially since cast iron may be prone to mineral scale buildup.
After plumber markup, cast iron material costs rise to approximately $12.50 to $30 per linear foot, while PVC ranges from about $0.60 to $7.50. The higher cast iron cost results from its heavier, more durable material composition.
For typical projects, replacing 30 feet of cast iron pipe including labor costs $375 to $900, whereas PVC replacements are generally more affordable due to lower material prices.
While installed costs can sometimes be similar, PVC’s lower material cost usually leads to reduced total expenses, especially on straightforward projects.
Additionally, PVC pipes are often favored because they are easier to install and require less labor and demolition, which can further reduce overall replacement costs.
Installation Differences and Labor Requirements
You’ll find that cast iron’s heavy weight considerably increases handling difficulty and labor time during installation compared to lightweight PVC. This is because cast iron components often require multiple stages of pressure buildup during their operation.
The complexity of cast iron joints and alignment demands more skilled labor, while PVC’s simpler solvent-welded connections reduce installation time.
Modern cast iron systems allow fittings to be adjusted post-installation, which can be advantageous during home remodels. Understanding these differences helps you plan for the labor intensity and scheduling of your project accurately.
Material Weight Impact
Although cast iron pipes offer durability, their substantial weight considerably influences installation methods and labor demands compared to lightweight PVC.
You’ll find cast iron’s high density requires heavy machinery or additional manpower for handling, increasing physical effort and safety precautions during installation. This weight also necessitates stronger structural supports and precise alignment to prevent joint stress.
Additionally, improper installation can lead to premature failure of cast iron piping systems. In contrast, PVC’s lightness allows easier manual handling, reducing fatigue and injury risk. You can install PVC with fewer workers, cutting labor costs and time.
Furthermore, PVC pipes simplify transportation and positioning, especially in confined spaces, enhancing installation efficiency. Additionally, PVC is resistant to chemical erosion, which further contributes to its suitability in various environments.
Understanding these material weight impacts helps you select the appropriate pipe type based on project logistics, labor availability, and safety considerations.
Labor Time Comparison
The substantial weight difference between cast iron and PVC pipes directly affects labor time during installation. Cast iron’s heavy, rigid sections require precise fitting, skilled labor, and more time for cutting, deburring, and jointing.
Handling and transporting cast iron demands additional workers and specialized equipment, increasing fatigue and reducing efficiency. Additionally, cast iron installations often require permits and inspections, adding administrative labor and time to the project.
Proper preparation, including gathering necessary tools and ensuring a clean workspace, can help mitigate delays in installation. Excavation and site preparation for cast iron pipes are also labor-intensive due to rigidity and extensive restoration needs.
In contrast, PVC pipes’ lightweight nature simplifies handling, allowing fewer workers and less equipment. Its solvent welding or push-fit joints speed up assembly and require less specialized skills. Wearing safety goggles and gloves during handling can improve worker safety and efficiency.
Excavation is often less extensive because of PVC’s flexibility. Modern trenchless methods and CIPP lining further reduce labor for PVC and cast iron systems, but overall, PVC installations consistently require markedly less labor time.
Installation Complexity Differences
When comparing installation complexity, cast iron demands significantly more labor skill and specialized tools than PVC. You’ll need heavy equipment like hoists and pipe cutters, plus precise techniques for coupling rubber-gasketed joints or using lead and oakum seals.
Cast iron’s weight and rigidity also make handling and positioning labor-intensive, increasing injury risk. In contrast, PVC is lightweight and flexible, allowing easier transport and installation in tight spaces.
You can cut and join PVC pipes with basic tools using solvent welding or push-fit systems, which need less expertise and cure quickly. Additionally, PVC’s high strength-to-weight ratio contributes to its ease of installation and reduced labor requirements.
Moreover, PVC piping systems benefit from flexibility that can absorb energy from pressure surges, enhancing system durability during operation.
Durability and Expected Lifespan of Both Materials
Because durability and lifespan critically impact plumbing performance, understanding how cast iron and PVC compare is essential.
Cast iron boasts superior strength and abrasion resistance but can corrode over time, especially in acidic or moist environments. Cast iron pipes typically last between 50 to 100 years, with their lifespan influenced by installation quality, soil conditions, water quality, and maintenance.
PVC resists corrosion and chemical damage, offering flexibility that reduces cracking risk in shifting soils. Both materials generally last 50 to 100 years, depending on installation quality and environmental factors. Its resistance to moisture and chemical exposure makes PVC particularly suitable for underground applications.
Key points to contemplate include:
- Cast iron requires regular maintenance to prevent rust and extend lifespan.
- PVC’s resistance to corrosion and flexibility often result in lower maintenance needs.
- Environmental exposure and installation practices critically influence the longevity of both materials.
Choosing between them depends on balancing these durability traits with your specific plumbing conditions.
Temperature Resistance and Fire Safety Considerations
Although both cast iron and PVC serve as common plumbing materials, their temperature resistance and fire safety characteristics differ markedly, impacting your choice depending on application demands.
Cast iron withstands temperatures exceeding 212°F without losing structural integrity, making it ideal for hot water and high-heat environments. It also offers durability where heat resistance is critical, which is essential in demanding settings.
Its robust nature also means it can handle higher system pressures commonly found in complex plumbing setups with pressure compatibility.
In contrast, PVC deforms above 140°F and can ignite at approximately 450°F, releasing toxic fumes when burned. You’ll find cast iron preferred in commercial kitchens and boiler drains due to its fire resistance and compliance with strict building codes, especially in fire-rated assemblies.
Additionally, cast iron handles thermal stress better, resisting cracking and thermal shock. PVC’s susceptibility to melting and toxic emissions limits its use where fire safety and high temperatures are concerns unless supplemented with fireproofing measures.
Physical Properties and Flexibility Analysis
You’ll notice cast iron’s heavy weight demands more effort during handling, while PVC’s lightweight nature simplifies installation. Additionally, the power supply requirements can differ due to the materials’ impact on system components.
The rigidity of cast iron offers strong structural support but limits flexibility, risking cracks under stress.
In contrast, PVC’s flexibility allows easier bending and better absorption of ground movement, making it ideal for dynamic environments. This lightweight characteristic also contributes to easier transport and reduced labor costs during installation.
Weight and Handling
When comparing cast iron and PVC pipes, their weight plays a crucial role in handling and installation efficiency. Cast iron pipes are considerably heavier, requiring mechanical assistance and increasing labor intensity.
PVC pipes’ lightweight nature reduces manpower needs and speeds up installation. This weight difference also affects transportation and safety on site. Consider these key points:
- Cast iron’s heaviness demands more physical effort, raising injury risks during handling.
- PVC’s light weight facilitates quicker installation and easier movement, lowering labor costs.
- The weight disparity influences long-term maintenance, with cast iron’s robustness balancing its handling challenges.
Understanding these factors helps you choose the ideal pipe material based on project scale, labor resources, and handling constraints. Additionally, using corrosion-resistant pipes such as PVC can enhance durability and reduce maintenance needs in water supply systems.
Rigidity Versus Flexibility
Because cast iron and PVC differ fundamentally in rigidity and flexibility, choosing between them hinges on your project’s structural demands and environmental conditions.
Cast iron offers exceptional rigidity and strength, ideal for high-pressure setups, while PVC’s flexibility suits installations requiring bending or ground movement absorption. However, PVC demands careful support to prevent deformation, especially under load or heat.
| Property | Cast Iron | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Rigidity | High; resists bending and expansion | Low; allows bending and molding |
| Temperature Range | Up to ~650°F; maintains strength | Up to ~140°F; softens above this |
| Installation Impact | Requires precise alignment | Easier, faster, but needs support |
Choose based on load, temperature, and flexibility needs. It is also important to check if the sump pump is functioning properly to ensure your installation remains effective during power outages.
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Impact
Although cast iron pipes offer robustness, they suffer from corrosion issues that compromise their longevity, especially in acidic or alkaline environments where rust buildup can increase maintenance demands and leak risks. Regular maintenance or timely repairs can extend its service life, but may require replacement sooner if neglected.
PVC pipes, on the other hand, are inherently corrosion-resistant, providing superior durability in chemically aggressive settings. Their flexibility minimizes cracking risk during ground shifts, making them suitable for variable soil conditions.
Environmentally, cast iron uses natural materials and is recyclable, but its manufacturing and heavy weight increase its carbon footprint. PVC’s lightweight nature reduces transportation emissions, though its petroleum base and limited recyclability raise sustainability concerns.
Key points to contemplate:
- Cast iron corrodes in harsh chemical environments; PVC remains chemically inert.
- Cast iron’s production is energy-intensive; PVC production emits toxic chemicals but is less energy-demanding.
- PVC’s lightweight reduces installation emissions; cast iron’s recyclability aids end-of-life sustainability.
Maintenance Needs and Repair Processes
Since cast iron and PVC pipes differ markedly in material properties, their maintenance and repair requirements vary accordingly. Cast iron needs frequent inspections for corrosion, rust, and leaks, while PVC demands less upkeep, focusing mainly on joint integrity and minor cracks.
The corrosion resistance of PVC significantly reduces the frequency and extent of repairs compared to cast iron. Repairs on cast iron are labor-intensive, costly, and slower due to its weight and rigidity.
In contrast, PVC repairs are quicker, simpler, and less expensive, benefiting from its lightweight and flexible nature.
| Aspect | Cast Iron | PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance | Frequent corrosion checks, blockage clearing | Low maintenance; inspect joints and cracks |
| Repair Complexity | Labor-intensive, requires heavy equipment | Simple, uses solvent welding or couplings |
| Repair Disruption | Longer timelines, may need bypass systems | Minimal disruption, often no full shutdown |
Chemical Resistance and Suitability for Various Applications
When selecting between cast iron and PVC for piping applications, understanding their chemical resistance is crucial to guarantee durability and performance. Cast iron offers moderate resistance but corrodes in acidic or alkaline environments, compromising longevity.
Choosing cast iron or PVC depends on chemical resistance needs to ensure pipe durability and performance. PVC excels against acids, salts, bases, fats, and alcohols but fails with chlorinated hydrocarbons, ketones, and acetone.
Compatibility depends on chemical exposure duration and conditions, which should be considered when choosing PVC. This makes PVC preferable for chemical handling and potable water systems, while cast iron suits high-pressure and heavy-duty uses.
Consider these points for application suitability:
- PVC withstands aggressive chemicals and outdoor exposure without corrosion.
- Cast iron endures higher temperatures and mechanical stresses but requires protective coatings.
- Both materials demand compatibility checks for specific chemicals to avoid failures or deformation.
Weight and Handling on Job Sites
You’ll notice cast iron pipes weigh considerably more than PVC, affecting how you transport and handle them on site.
This weight difference directly impacts the labor and equipment needed for installation. Cast iron pipes are heavier and thus require more effort and often specialized equipment compared to the lightweight PVC pipes.
Understanding these factors helps you choose the most efficient material for your project’s logistics and workflow. The heavier weight of cast iron pipes also makes them less suitable in earthquake-prone areas.
Material Weight Comparison
Although cast iron pipes provide robust durability, their significant weight creates challenges in handling and transportation on job sites. You’ll find cast iron requires more manpower or mechanical assistance for lifting and positioning, which can increase labor costs and slow project timelines.
In contrast, PVC pipes are notably lighter, allowing you to transport and maneuver them manually with less physical strain and reduced risk of injury. This lightness improves job site efficiency and lowers logistical complexity.
Key considerations include:
- Cast iron’s heavy weight demands additional labor and equipment, raising handling and transportation expenses.
- PVC’s lightweight nature facilitates quicker staging and safer manual handling.
- The reduced weight of PVC lowers overall project costs and minimizes worker fatigue.
Ease of Installation
Handling and installing pipes on job sites directly affects project efficiency and labor demands. Cast iron pipes require more manpower due to their heavier weight and brittleness, demanding careful support to prevent cracking during transport and placement.
You’ll often need specialized lifting equipment and skilled labor for precise alignment and sealing, increasing installation time and labor intensity.
In contrast, PVC pipes are lighter, flexible, and resilient, allowing fewer workers to carry and maneuver them safely with minimal mechanical aid. Their modular design speeds up alignment and joining, reducing labor time and costs. Additionally, PVC’s easier handling lowers injury risk and fatigue.
Storage and transport are simpler with PVC, which requires less space and handling clearance. Overall, PVC offers a faster, safer, and less labor-intensive installation process.
Long-Term Cost Implications and Value Assessment
When evaluating long-term cost implications and value between cast iron and PVC pipes, you must consider initial expenses alongside maintenance, durability, noise control, and fire safety factors.
While PVC offers lower upfront material and installation costs, it may incur higher expenses due to noise mitigation and complex firestopping requirements. Additionally, PVC’s lightweight and easy installation can reduce labor time in new construction projects.
Cast iron’s durability and inherent fire resistance can reduce maintenance and insurance costs over time, despite higher initial investment. Key considerations include:
- Maintenance and durability: Cast iron resists fire and noise better but risks corrosion; PVC resists corrosion but may degrade under extreme conditions.
- Noise impact: Cast iron pipes reduce noise by approximately 10 dB, potentially lowering mitigation costs.
- Fire safety costs: Cast iron requires simpler firestopping; PVC demands costly intumescent materials and faces stricter regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Cast Iron and PVC Pipes Recyclable After Use?
Yes, you can recycle both cast iron and PVC pipes after use. Cast iron pipes are highly recyclable, allowing you to reuse the material indefinitely without losing quality.
PVC pipes are recyclable too, but their process is more complex due to additives and contamination risks, often resulting in downcycling. While cast iron recycling is straightforward and efficient, PVC recycling demands advanced sorting and emerging technologies to enhance material recovery and environmental benefits.
How Do Noise Levels Compare Between Cast Iron and PVC Pipes?
You know what they say: silence is golden. When it comes to noise levels, cast iron pipes consistently outperform PVC by about 6 to 10 decibels, averaging 8 dBA quieter. This is due to cast iron’s higher density, which absorbs sound better.
PVC’s lighter mass lets more noise escape, especially in horizontal runs. Even with insulation, PVC rarely matches cast iron’s superior sound dampening in plumbing systems.
Which Material Is Better for Underground Sewer Applications?
For underground sewer applications, you should consider load-bearing and environmental factors. If your project demands high structural strength and fire resistance, cast iron performs better, especially under heavy earth or traffic loads.
However, if you want corrosion resistance, lighter weight, and easier installation, PVC is advantageous. You’ll need to account for PVC’s thermal expansion and fire restrictions.
Can PVC Pipes Be Used in Potable Water Systems?
Yes, you can use PVC pipes for potable water systems, but with conditions. PVC must meet strict certifications like NSF/ANSI 61 to guarantee it doesn’t leach harmful chemicals into drinking water.
However, many local codes restrict PVC use inside homes for potable water, favoring CPVC or other materials better suited for hot water and compliance. PVC is commonly approved for underground cold water service lines outside buildings, provided it meets pressure and safety standards.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Manufacturing Cast Iron Vs PVC?
You might think all manufacturing impacts are equal, but they differ greatly. Producing cast iron consumes vast energy, emitting significant CO2, SO2, and heavy metals due to blast furnace use.
PVC manufacturing relies heavily on petrochemicals, releasing dioxins, chlorine compounds, and VOCs, posing air and water risks. Cast iron’s recyclability reduces its long-term footprint, while PVC’s complex additives complicate recycling and often lead to harmful waste management practices.
Final Verdict: PVC or Cast Iron for Your Plumbing Needs
Choosing between cast iron and PVC is like picking the right tool for a craftsman’s task; each excels under different conditions. Cast iron stands firm like an old oak, offering durability and fire resistance, while PVC flows with flexibility and ease, adapting to modern demands.
By understanding their unique strengths in cost, installation, and maintenance, you can confidently select the material that best fits your project’s technical and long-term needs.
- INCLUDES/ SPECIFICATIONS: (1) Round, Clear PVC Dust Collection Pipe; 4” O.D. , 5/64 inch wall…
- APPLICATIONS: It can be used in conjunction with couplers to form an extension or foundation for…
- FEATURES: This PVC pipe increasing productivity while utilizing see-thru visibility of air flow for…
- 1/2 INCH X 72 INCH BLACK PIPE 4 PACK: Design ambitious projects for your bedroom, bathroom, kitchen,…
- UNLEASH YOUR CREATIVITY and bring the vintage industrial style into your home, office, garage,…
- HIGH QUALITY, DURABLE INDUSTRIAL PIPE FITTINGS. You will know Pipe Décor parts and accessories when…
Last update on 2026-03-02 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API