Last Updated on April 30, 2025
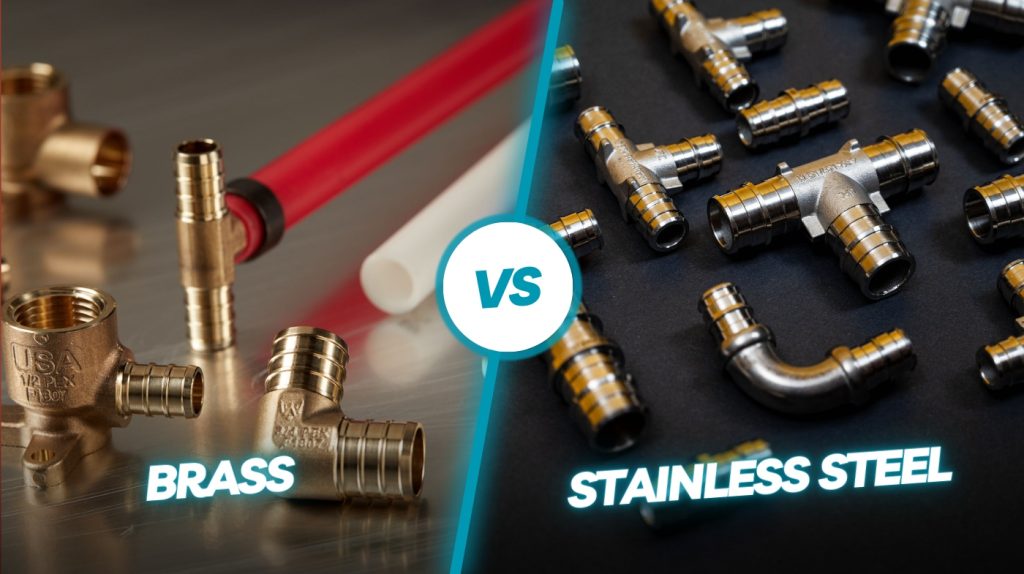
When choosing between brass and stainless steel PEX fittings, you’ll find stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, especially against dezincification and chemical exposure, ensuring longer system life.
It also boasts higher strength with better hydraulic efficiency from optimized designs, plus greater temperature tolerance up to 400°F versus brass’s typical 180°F limit.
While brass fittings cost less upfront, stainless steel delivers better durability and fewer maintenance issues. Exploring further reveals detailed performance and cost implications for your specific plumbing needs.
- 【Package Includes】: Pex B Fittings Combo includes 12pcs 1/2″ PEX Elbows, 12pcs 1/2″ PEX Tees,…
- 【Non-Pollution】: Lead free brass pex fittings, comply with drinking water standard. ASTM F1807…
- 【Extra-Long Service Life】: High-quality brass pex 90 degree elbow & tee & coupling, resists…
Key Takeaways
- Stainless steel PEX fittings resist corrosion better than brass, avoiding dezincification and ensuring longer system integrity.
- Stainless steel offers higher strength and durability, with superior mechanical properties under stress compared to brass.
- Hydraulic performance is improved with stainless steel due to larger flow area and optimized bend designs versus brass fittings.
- Stainless steel fittings tolerate higher temperatures (up to 400°F) and broader chemical exposure than brass fittings.
- Although brass fittings cost less initially, stainless steel fittings provide better long-term value through durability and reduced maintenance.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
When comparing corrosion resistance in PEX fittings, you’ll find stainless steel outperforms brass due to its chromium oxide layer, which provides robust protection against various corrosive agents.
Brass, primarily a copper-zinc alloy, relies on copper’s oxide layer for corrosion resistance but remains susceptible to dezincification—zinc leaching that degrades standard brass, especially in thin-walled crimp fittings or aggressive water chemistries.
DZR (Dezincification Resistant) brass variants mitigate this but still face localized corrosion risks due to limited metal surface area when paired with PEX pipes. These variants include added elements like arsenic or antimony to improve their dezincification resistance.
Brass fittings depend on copper oxide for protection but can suffer from dezincification in harsh water conditions. Stainless steel fittings resist dezincification entirely and maintain stability across wider pH and temperature ranges.
They also avoid zinc-related corrosion mechanisms, making them more reliable in acidic or chlorinated environments. Consequently, stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, extending long-term system integrity under variable conditions.
Strength and Durability Differences
Although both brass and stainless steel PEX fittings offer reliable performance, you’ll find notable differences in their strength and durability that influence their suitability for specific applications.
Stainless steel exhibits higher tensile strength and hardness than brass, providing superior resistance to mechanical stress and impact. This makes stainless steel fittings more durable under extreme conditions and higher internal pressures.
Moreover, stainless steel fittings are less vulnerable to chemical degradation, which is a critical factor given PEX’s susceptibility to chemical exposure.
Brass, while strong, is prone to dezincification and corrosion in certain water conditions, reducing its longevity. Stainless steel maintains consistent mechanical properties across diverse environments, requiring less maintenance.
Additionally, stainless steel’s thermal expansion differs from brass, which may affect performance under temperature fluctuations.
When durability and strength are paramount, especially in harsh or chemically aggressive environments, stainless steel fittings justify their higher cost by delivering enhanced reliability and extended service life compared to brass alternatives.
Note that metal fittings outperform plastic fittings in strength and flow characteristics, further emphasizing stainless steel’s advantages.
Flow Rate and Hydraulic Performance
Beyond strength and durability, the flow rate and hydraulic performance of PEX fittings play a significant role in system efficiency and fixture functionality.
You’ll find that plastic PEX fittings reduce flow due to smaller inner diameters and insertion design, which increases turbulence and friction, especially in 90-degree elbows.
Stainless steel fittings, however, provide a 23 to 36% larger flow area than poly PEX, minimizing friction loss with optimized sweep bend elbows. This design reduces pressure drops and maintains higher system pressure, ensuring fixtures operate effectively under simultaneous demand.
Although brass and stainless steel share similar diameters, stainless steel’s superior hydraulic design offers better flow characteristics. Furthermore, stainless steel fittings eliminate the need for dual inventories in installations due to their versatile applications.
Temperature and Chemical Resistance
You’ll notice brass PEX fittings handle typical hot water temperatures well but may struggle with extreme thermal cycling and chemical exposure. Brass PEX fittings are made from lead-free DZR Brass, ensuring safety for drinking water applications.
Stainless steel fittings, on the other hand, offer superior durability across a wider temperature range and resist corrosive environments more effectively. Let’s analyze how these differences impact performance and longevity under demanding conditions.
Temperature Range Comparison
When selecting PEX fittings, understanding the temperature range of brass versus stainless steel is essential for ensuring system reliability.
Brass fittings typically handle temperatures up to 200-250°C (392-482°F), though many brass PEX fittings, like F1807, limit operation to 180°F (82°C). It is important to check manufacturer specifications as exceeding the maximum temperature can compromise integrity.
Stainless steel fittings surpass brass in temperature resistance, maintaining integrity in more extreme environments and exhibiting superior thermal stability.
You’ll find stainless steel better suited for high-temperature applications due to its lower thermal expansion coefficient and enhanced durability under thermal stress.
While brass offers cost advantages, its temperature limitations restrict usage in demanding conditions.
Consequently, if your system faces significant thermal fluctuations or elevated temperatures, stainless steel fittings provide more reliable performance and longer service life, ensuring ideal safety and efficiency.
Chemical Exposure Durability
Although both brass and stainless steel PEX fittings offer significant chemical resistance, their performance varies depending on the specific chemical environment and temperature conditions
You’ll find dezincification-resistant (DZR) brass alloys effectively prevent zinc leaching in chlorinated or mildly acidic waters, maintaining durability.
Stainless steel fittings, however, provide superior resistance against a broader chemical range including acids, alkalis, and chlorides thanks to their chromium oxide passive layer, which also prevents pitting and crevice corrosion.
Because stainless steel contains no zinc, it avoids dezincification entirely, ensuring greater long-term stability.
Both metals pair well with PEX tubing, which itself resists many chemicals but requires pressure derating at elevated temperatures. It is important to follow manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure compatibility and prevent system failures.
When selecting fittings, consider that stainless steel generally outperforms brass in chemically aggressive environments, offering enhanced corrosion resistance and longevity under variable temperature and chemical exposure conditions.
Thermal Cycling Resistance
The chemical resistance of brass and stainless steel PEX fittings directly influences their ability to withstand thermal cycling stresses. Brass exhibits lower thermal expansion and good ductility, maintaining joint integrity under repeated cycles up to 210°F.
Stainless steel tolerates higher temperatures (up to 400°F) and offers superior thermal fatigue resistance due to a higher modulus of elasticity. However, stainless steel’s lower thermal conductivity slows heat transfer, potentially reducing thermal stress at fittings.
Additionally, the corrosion resistance of brass fittings ensures long-term durability in plumbing systems exposed to various water qualities.
| Property | Brass | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature (°F) | ~210 | ~400 |
| Thermal Expansion | Lower | Moderate |
| Thermal Conductivity | ~109 W/m·K | ~15 W/m·K |
| Fatigue Resistance | Good ductility | Excellent endurance limits |
Installation and Compatibility Factors
When selecting between brass and stainless steel PEX fittings, you need to guarantee dimensional compatibility with your existing tubing to maintain system integrity.
Stainless steel fittings often simplify inventory management by offering durability that reduces the need for multiple material types on-site.
Additionally, both fitting types use similar tooling, but stainless steel’s robustness can lower installation risks and tool wear.
The increased flow improvement of up to 23% observed with stainless steel sweep 90 elbow designs further supports their efficiency advantage in fluid dynamics.
Fitting Dimensions Compatibility
Since both brass and stainless steel PEX fittings follow standardized nominal sizing, you can expect consistent dimensional compatibility across common PEX tubing sizes like 1/2”, 3/4”, and 1”.
Both fitting types adhere to strict ID and OD standards, ensuring a precise fit that prevents leaks and maintains system integrity. You’ll find stainless steel fittings match brass counterparts dimensionally, allowing seamless substitution without redesigning layouts.
Installation tolerances are tight for both materials, supporting secure crimp or clamp ring connections. While external dimensions align, slight internal shape differences may influence flow characteristics, with stainless steel often providing smoother passage.
Additionally, stainless steel fittings are known for their superior corrosion resistance compared to brass, which can be susceptible to dezincification
This dimensional conformity extends to all PEX tubing types and common connection styles, ensuring reliable, pressure-resistant joints without compromising performance or requiring special adjustments during installation.
Inventory and Tooling Impacts
Although managing inventories for brass and plastic PEX fittings demands handling distinct materials separately, stainless steel fittings offer a unified solution that streamlines storage and reduces complexity.
You’ll save on storage space and handling costs with stainless steel’s standardization. Tooling-wise, stainless steel requires fewer specialized tools than brass and plastic combined, simplifying your toolkit and installation process. Its corrosion resistance also protects your tools, extending their lifespan.
Additionally, stainless steel’s long lifespan means replacements and maintenance are needed less frequently, further reducing overall costs.
| Aspect | Brass & Plastic | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory | Dual, complex | Unified, simplified |
| Tool Variety | Multiple, specialized | Fewer, compatible tools |
| Installation | Longer, tool-dependent | Quicker, streamlined |
| Tool Durability | Moderate, prone to corrosion | High, corrosion-resistant |
Application Suitability and Use Cases
When selecting PEX fittings, understanding their application suitability hinges on factors like corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and hydraulic efficiency.
Stainless steel fittings excel in corrosive or acidic water conditions, such as well water or hydronic heating systems, due to their chromium oxide passivation layer, which prevents dezincification—a common issue with brass.
Additionally, stainless steel fittings are known for their superior corrosion resistance compared to brass, making them highly reliable in harsh environments. Their material composition also allows them to withstand higher pressures, enhancing their performance in demanding applications.
Stainless steel fittings resist corrosion and dezincification, ideal for acidic or well water applications. Their superior tensile strength, roughly double that of brass, enables use in high-pressure and industrial settings without deformation risks.
Hydraulic efficiency also favors stainless steel, offering 23–36% greater flow area through thinner walls and optimized elbow designs, reducing turbulence and friction loss. Brass fittings suit standard residential applications with moderate pressures and quality water, but falter in chemically aggressive environments.
You should choose stainless steel for demanding systems, prioritizing durability, flow performance, and chemical resistance.
Maintenance and Replacement Considerations
Since maintenance demands directly impact system reliability and lifecycle costs, understanding the corrosion susceptibility and environmental effects on PEX fittings is essential.
Brass fittings are prone to stress corrosion cracking, rust, and scale buildup, especially in humid or acidic conditions, necessitating frequent inspections and dry, ventilated storage. You’ll need to monitor condensation and exposure to heat, as excessive temperatures accelerate degradation.
Additionally, selecting the appropriate PEX fitting type based on application can influence durability and maintenance needs. Regular inspections can identify corrosion early and prevent significant issues.
Stainless steel fittings, however, resist corrosion better, reducing inspection frequency and extending service life under thermal and mechanical stress.
If you detect defects in brass fittings, prompt replacement is critical to avoid leaks and failures. Given brass’s shorter lifespan in corrosive environments, switching to stainless steel or plastic alternatives can lower long-term costs and enhance system reliability, especially where well water or high humidity is a factor.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Stainless Steel PEX Fittings Recyclable Compared to Brass?
Yes, you can recycle stainless steel PEX fittings effectively. Stainless steel’s recycling process is straightforward, involving melting without degrading its properties, which helps conserve energy and raw materials.
While brass is also recyclable, stainless steel’s recyclability is more environmentally favorable due to lower energy demands and a more developed recycling infrastructure.
Choosing stainless steel fittings supports sustainability by reducing environmental impact and enhancing resource efficiency throughout their lifecycle.
How Do Brass and Stainless Steel PEX Fittings Impact Water Taste?
Imagine sipping crystal-clear water free from any metallic aftertaste. When you use brass fittings, acidic water can corrode them, releasing copper and zinc ions that cause a metallic flavor and blue-green stains.
Stainless steel fittings resist corrosion and keep water taste neutral, even in low pH environments.
To maintain clean taste, you should flush your system regularly and test water chemistry before choosing fittings, ensuring long-term safety and flavor integrity.
Do Stainless Steel Fittings Require Special Tools for Installation?
Yes, you’ll need special tools to install stainless steel PEX fittings. Specifically, PEX clamp tools are required to cinch stainless steel clamp rings securely onto the tubing, ensuring a watertight seal.
These tools are often designed to work across various PEX sizes and are calibrated for precise clamping. Using the correct tool is essential for reliable, corrosion-resistant connections, and it also simplifies installation, often enabling one-handed operation for efficiency.
Can Brass or Stainless Steel Fittings Be Used With Radiant Floor Heating?
Imagine your radiant floor heating system as a finely tuned orchestra, where every fitting plays a crucial role. You can confidently use brass or stainless steel fittings—they both stand up well to heat and pressure.
Brass offers strong corrosion resistance and suits higher temperatures, while stainless steel boasts excellent durability and handles extreme conditions.
Just verify you install them correctly with proper tools and consider dielectric unions to prevent galvanic corrosion when mixing metals.
What Is the Weight Difference Between Brass and Stainless Steel PEX Fittings?
You’ll find that stainless steel PEX fittings weigh about 5–15% less than brass ones of the same size due to their lower density.
This weight difference can make handling and installation easier, especially for larger fittings or bulk projects. However, keep in mind that design factors like wall thickness and grade variations influence exact weights.
Choosing Fittings That Last: Performance Over Price
When choosing between brass and stainless steel PEX fittings, you’ll find stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for harsh environments.
Brass, while strong and cost-effective, may face dezincification over time. Your decision should weigh installation needs, budget, and long-term performance.
By understanding these technical differences, you can guarantee reliable plumbing that balances durability with cost—debunking the myth that cheaper always means sufficient for all applications.
- 【Package Includes】- Pex brass crimp fitting combo includes 10pcs 1/2″ tees”T”, 10pcs 1/2″…
- 【Premium Material】- They are made from durable brass and they can be used for PEX pipes in…
- 【Easy Installation】- This 30pcs 1/2″ brass pex fittings can be easily installed without flame,…
Last update on 2026-01-29 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API